Demystifying QR Codes: How Those Pixelated Squares Actually Work
Chang

You scan a QR code and a website opens. You scan a different one and get a string of characters that means nothing. Same type of code, completely different result. What is actually going on?
If you work in maintenance or facility management, this matters. QR codes are on your equipment, your spare parts shelves, your safety signage. Some open in a browser, some only work with a specific app, and some seem to do nothing at all. Here is why.
A QR Code Is Just a Container for Text
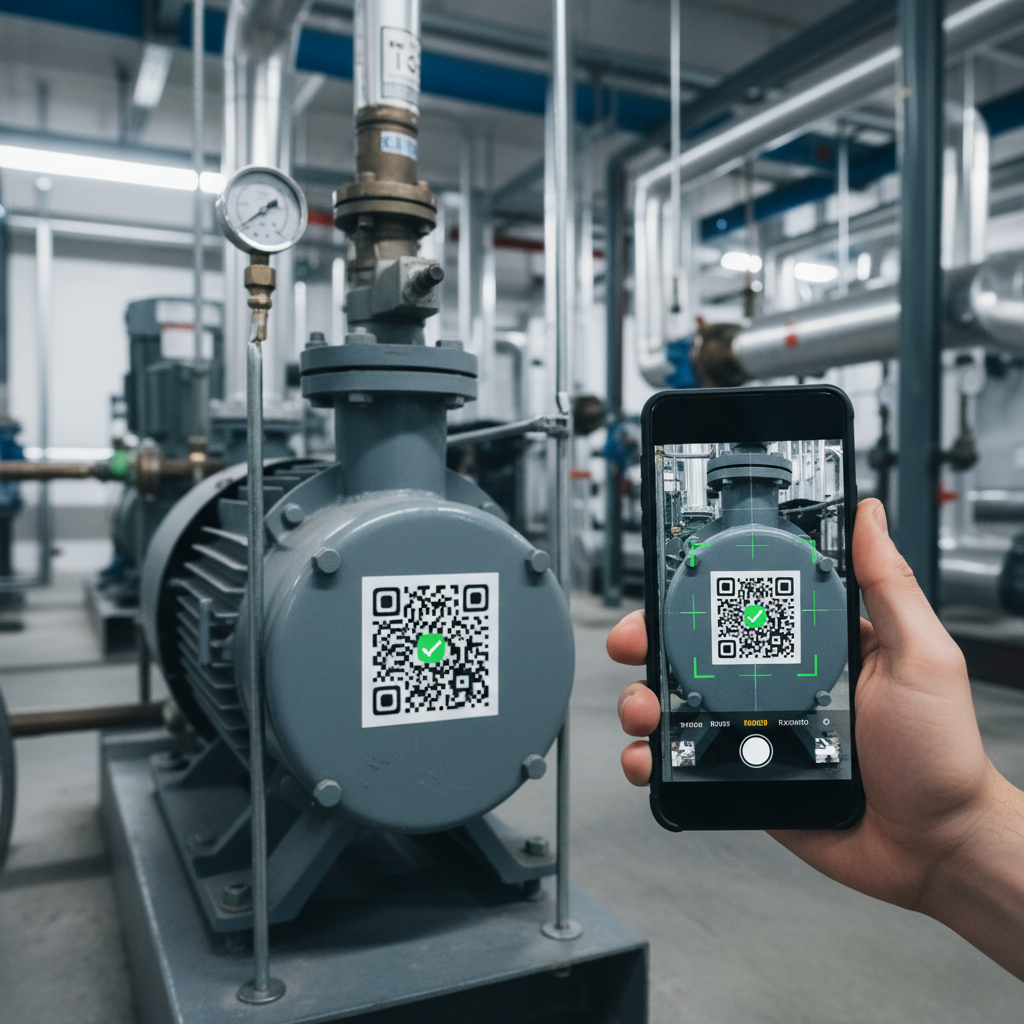

A QR code holds a string of characters. That is it. No executable code, no hidden instructions. It could contain a URL like https://example.com/asset/abc123, a custom URI like myapp://asset/abc123, or plain text like AHU-03-LEVEL-2-CHILLER-PLANT. The QR code does not care what the text is. It just stores it.
The black and white squares are binary data arranged per the QR standard (ISO/IEC 18004). The three large corner squares help your camera orient the code from any angle. The smaller patterns handle error correction, so a QR code can lose up to 30% of its surface and still scan. That durability is why QR beats traditional barcodes in plant rooms, rooftops, and mechanical floors where grease, dust, and UV take their toll.
How Your Phone Decides What to Do
Once your phone reads the text, it makes a simple decision based on what the text looks like:
- Starts with https://: your phone opens it in the browser. This is why most QR codes you encounter open websites.
- Starts with a custom scheme like
cerev://asset/abc123: your phone looks for an installed app that handles that scheme. No app installed? You see the raw text, which looks like gibberish. - Plain text: your phone just displays it. Without an app to interpret it, it is meaningless to you.
This explains a common frustration. One technician scans a QR code and sees full asset details. Another scans the same code on a different phone and gets nothing useful. The difference is not the QR code. It is what is installed on each phone.
The Real Magic: UUID to Database
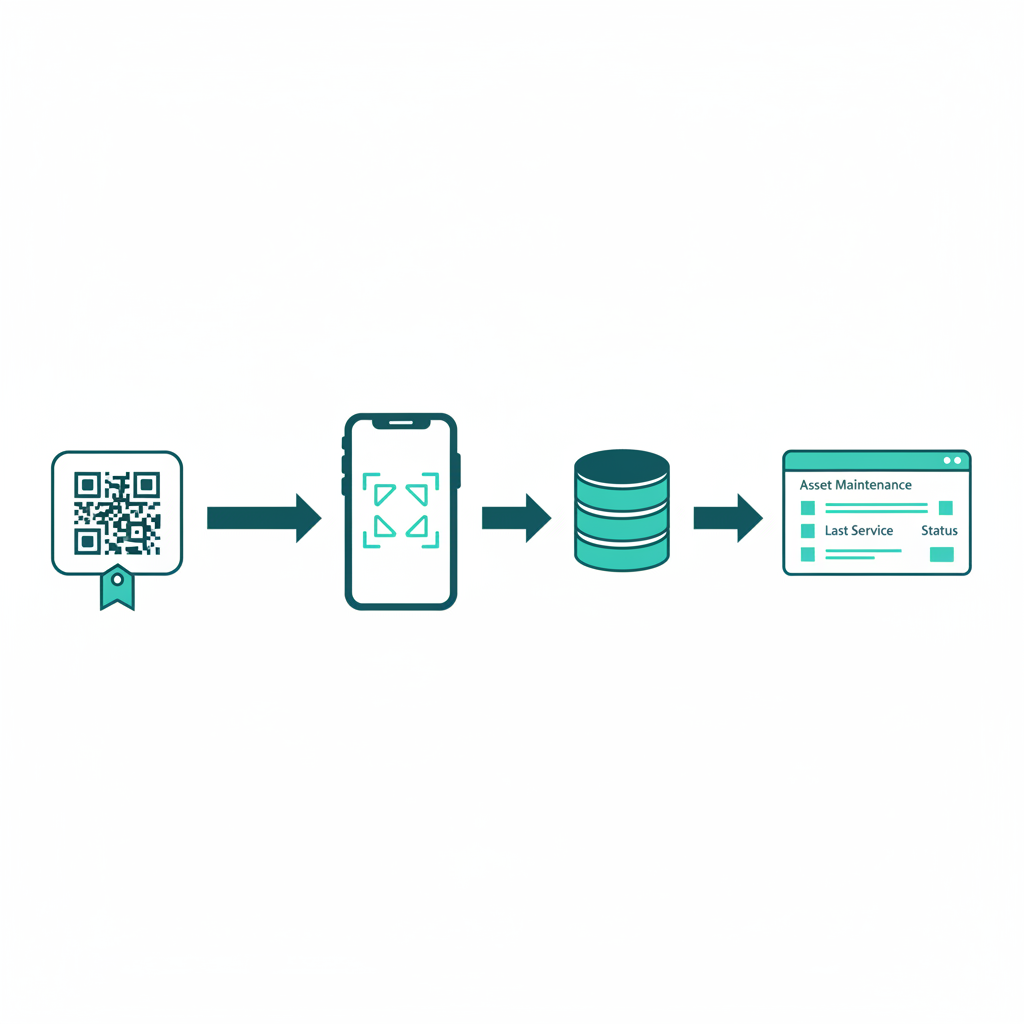
The QR code is just the delivery mechanism. The real value is what it delivers: a UUID (Universally Unique Identifier) like f47ac10b-58cc-4372-a567-0d02b2c3d479. Every UUID ever generated is practically unique, so every asset in your facility gets a globally unique identity with no collision risk.
Here is the full chain when you scan:
- Phone reads the QR code and gets a URL like
https://app.cerev.com/asset/f47ac10b-58cc-4372-a567-0d02b2c3d479 - The app extracts the UUID from the URL
- The UUID hits a database query that finds the matching asset record
- The database returns everything: maintenance history, documents, PM schedules, open work orders, spare parts, downtime records
- All of it displays on your screen in under two seconds
A tiny sticker on a pump connects to years of maintenance data. The QR code on the physical equipment is the bridge between the real world and the digital record.
Putting It Into Practice
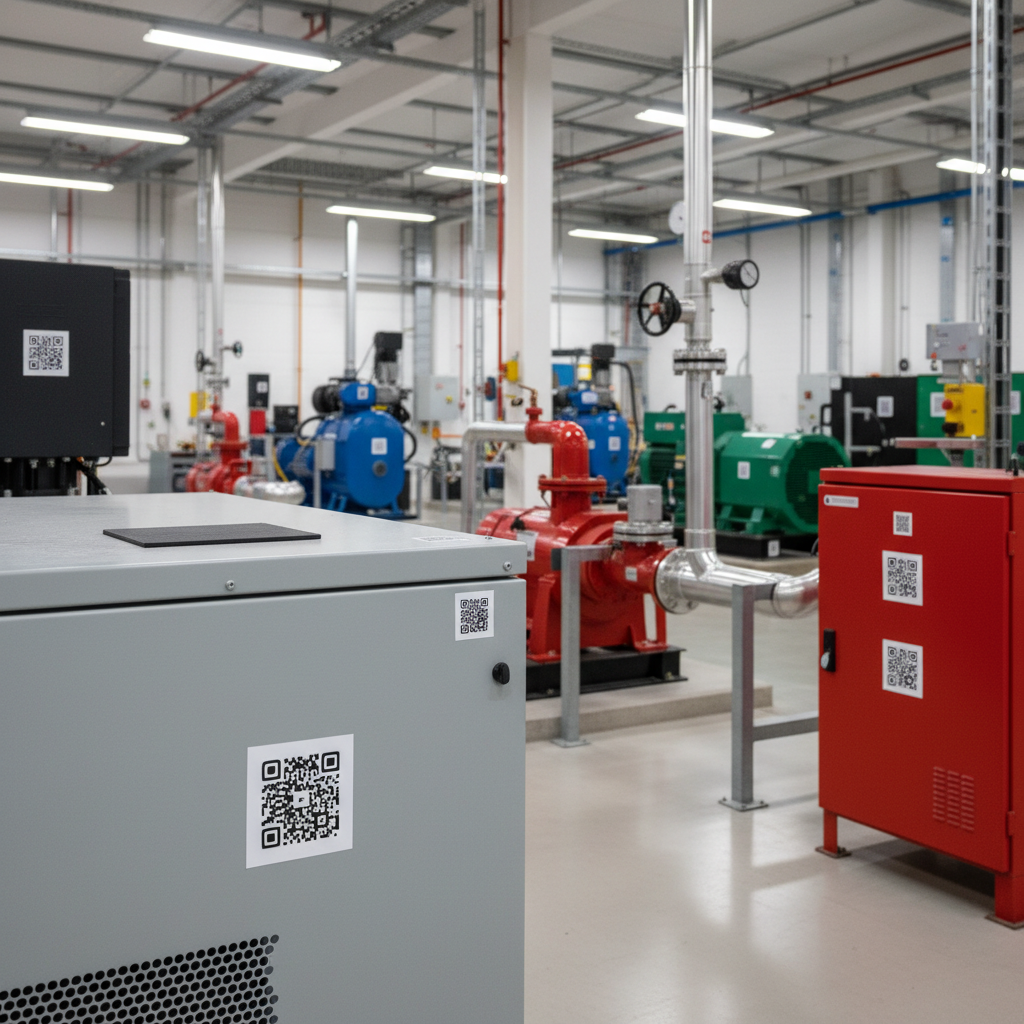

Generate QR labels from your CMMS. When you create an asset record, the system assigns a UUID and generates a QR code containing it. One-to-one mapping, no manual entry, no mismatch.
Pick the right label material. Standard adhesive for indoor air-conditioned spaces. Polyester or aluminium with UV-resistant printing for outdoor, plant rooms, or harsh environments. Place labels consistently, somewhere visible and accessible without ladders.
Build the scanning habit. Your technicians already know how to scan. The training is not about how, but why: scanning the asset QR before starting any work order ensures every activity links to the correct record automatically. That builds the maintenance history that makes your data valuable over time.
In Cerev CMMS, every asset gets a unique QR code at registration. Technicians scan it and instantly see the full record: history, documents, PM schedules, open work orders, and specs. They can raise a new work order directly from the scan, automatically linked to the right asset. The same system extends to inventory, where scanning a spare part shows stock levels, reorder points, and which assets use it.
The Bottom Line
The whole mechanism is three steps:
- QR code holds text, usually a URL with a unique identifier
- Your phone decides what to do: open browser, launch app, or show raw text
- A database does the rest: the identifier looks up everything about that asset
The value is not in the QR code itself. It is in the data behind it. Tag your critical assets, build the scanning habit, let the data accumulate. The QR code is just the key. The real treasure is the maintenance database it unlocks.
Ready to optimize your maintenance operations?
Get in touch with our team to discuss how Cerev CMMS can help streamline your maintenance workflow and reduce costs.